Choosing a Certification Body (CB) should be considered as an opportunity to question and verify the capabilities of the team that will be assessing and auditing your organization each and every year. This process can be daunting, especially to those of us who are new to the industry. ISOUpdate has a Directory of CB’s you can use to start your hunt, but we understand it might be confusing if you don’t already know what to look for and what questions to ask during the process. Here’s an assorted list of some questions that you need to ask your potential Certification Body.
Are you Accredited?
This should be the first and most important question you ask your CB when you are requesting quotes and determining who to select as your future CB. Confirm that the organization you are working with is accredited to ISO/IEC 17021 to ensure that your certification will be recognized. ISO/IEC 17021 is the conformity assessment standard that applies to bodies providing audit and certification of management systems.
Where will my certification be recognized?
If you are working with international suppliers or looking to do business in a certain country, you will need to ensure your new certification is recognized internationally. Ensuring your certification body is accredited by an Accreditation Body that has joined the IAF Multilateral Recognition Agreement (MLA) will confirm that your certification is recognized globally, but more specifically, in the markets you are interested in pursuing.
Can you supply a Letter of Certification Intent?
If you have been asked by an organization to obtain an ISO certification to do business with them, it would be worth pursuing a letter of certification intent to then offer your supplier for the time period leading up to your achievement of certification. This may be sufficient for the supplier as proof of your active commitment to becoming certified, and sufficient to start a contract with your organization for work.
What is the requirement of QMS maturity before certification can take place?
A Certification Body cannot implement a system for your organization, it can only audit an existing system. You may need the services of an Internal Auditor or Consultant to help your organization meet the requirements of the standard before you can move forward with your CB. In general, if you are running a successful business, you are already achieving a large portion of the standard, but an Internal Auditor or Consultant will be able to maximize efficiency, reduce documentation and wasted time and energy to ensure you meet and exceed all requirements. Some CB’s may require your system to be in place for a certain time period before they can audit it – ensure you are able to meet those deadlines.
What is your NPS for client satisfaction?
NPS or Net Promoter Score is a metric that organizations use to measure customer satisfaction. Organizations ask current clients their likelihood to recommend this organization to a friend. This is a great metric to consider when picking any organization you are planning to work with, as it indicates overall customer satisfaction of the whole process when dealing with a company. High NPS’s can give you, a potential client, a good indication of what you can expect from this company.
Other important customer service related questions you should be asking:
- How flexible can you be in terms of scheduling issues? Can you accommodate our expected registration date, or close to it?
- If we have questions and call in, can we expect a prompt response?
- What happens if we have a difference of opinion with one of your auditors? Who do we contact?
If your organization has a deadline to meet or an expiration to worry about for recertification, you will need to make that clear to the sales representative when they are quoting you a price. Time constraints will be a factor when they are selecting available auditors.
It is also valuable to know who your point of contact will be throughout the certification process, especially if you and your auditor come to a disagreement. This stage in your quoting journey is a good opportunity to understand what levels of communication this organization has for dealing with common questions, scheduling, and non-conformities.
What relevant industry experience do you have?
This question is especially pertinent if you are working in a specialised industry. Having an auditor who is familiar with your industry will make the whole process much easier.
Do you have local auditors?
Having a local auditor is an extreme advantage to you as a client, as it reduces the expenses incurred during your surveillance audits. A local auditor will have reduced travel, accommodation, and food expenses.
Other Questions to ask related to your auditor:
- Does the registrar use the same lead auditor/auditors each time?
- How many auditors would you use on this particular project?
- What is the frequency of surveillance audits and what is covered?
- Can we meet the auditors who would work on this project? And could we interview the lead auditor assigned to our company?
- Are travel and subsistence expenses built-in or additional? And if they are additional could you quote me an estimated figure?
You may want to dive into the CB’s process for hiring auditors; most certification bodies are extremely particular about who they hire as auditors, but it might be worthwhile to ask their base level of experience needed. Another important note to consider if your organization is pursuing re-certification, are you maintaining impartiality with your auditor team? The purpose of certification audits is to have an impartial, outside view of your QMS to eliminate bias. While it is wonderful if your organization has a pre-existing and positive relationship with your auditor, it can sometimes create bias. Consider switching up your auditor every few years and don’t become too reliant on your current third-party auditor to ensure you are getting the most out of each certification audit.
Do you offer certification to other standards? Do you offer integrated audits for more than one standard?
If you are looking to achieve ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 for example, having an integrated audit could be an option for your organization to save costs and time.
What sort of “off-site” time (such as report preparation, document reviews, etc.) could we be charged for?
Understanding the entirety of the process for auditing is important. Certification is not just an individual looking at your documents. They are taking a sample of your work and understanding how you effectively run your business using the requirements of an international standard. Auditors spend hours before and after each audit, preparing, going through the evidence, reporting findings, and interpreting the standard. By understanding this, you are able to better understand the quoting process, and the variables in place with each and every audit. By asking what is included in the quote, and even understanding the role and administration involved in the process, these numbers make much more sense.
Do you offer training for the standard you are looking to obtain?
If your organization wants to maximize your system, having your management team and employees attend training to fully understand the processes and guidelines of the standard is highly recommended.
For example, in ISO 9001:2015, there is increased attention on the involvement of upper management to ensure the success of the QMS. Upper management is required to have an active interest in the system and is responsible for ensuring its success. Attending training can only help your organization more easily obtain your certification.
How do you determine how much time to spend on a full system/surveillance audit?
This question should make or break your decision-making process, and it will confirm to you if your potential CB is truly accredited to ISO/IEC 17021. Organizations who are accredited are required to quote audit days based on the number of employees your organization has on staff and the risk level of your management system. Ensure you know the exact and correct number of employees you employ when you are in the quoting phase, as this will be asked. Discrepancies in quotes from the initial quote to actual billing are often due to misrepresentation from the organization on the true number of employed staff. To avoid surprises, ensure your number is accurate.
Summary
These are some key questions to ask prior to employing a CB. They have been designed with the intent to give you valuable insight into the CB, which is critical to selecting the right registrar for your organization’s needs. These are generic questions to help your organization by directing your questioning to ensure you are well informed about their practices. We highly encourage you to customize each and every question to fit your company’s agenda.







 Avital Koren is the Director of
Avital Koren is the Director of 

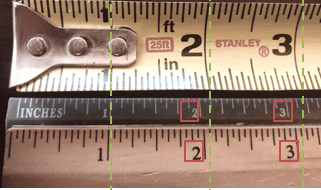 In this image, you will notice that at 1 inch, all rulers are measuring the same. But look at the 2- & 3-inch marks? They are all different. Which is the right measurement?
In this image, you will notice that at 1 inch, all rulers are measuring the same. But look at the 2- & 3-inch marks? They are all different. Which is the right measurement? Calibration stickers are the easiest way to identify your equipment and tools. The picture here is a snapshot of items you can find in google when searching for “calibration stickers”. You choose which best suits your organization and then start using it on all items that are calibrated. This is an easy way for everyone to know when to get the item calibrated.
Calibration stickers are the easiest way to identify your equipment and tools. The picture here is a snapshot of items you can find in google when searching for “calibration stickers”. You choose which best suits your organization and then start using it on all items that are calibrated. This is an easy way for everyone to know when to get the item calibrated.



